<변수와 함수와의 관계>
1. 함수 타입의 변수
<script>
function hello(name) {
alert("안녕하세요 " + name + "님");
}
function hello2(name) {
alert("안녕 " + name + "님");
}
var func = hello; // 특정 변수에 함수타입의 데이터를 지정
func("javjaman"); // 함수타입을 리터럴로 생각하면 됨.
</script>2. 함수 타입의 파라미터
<script>
function hello(name) {
document.write("안녕하세요 " + name + "님<br>");
}
function hello2(name) {
document.write("안녕 " + name + "님<br>");
}
// 2. 함수 타입의 파라미터
function myFunc(name) { // 콜백함수
// console.log(typeof name)
name("네임호출");
// 이렇게 작업하지 않을 경우
// name is not a function
}
myFunc(hello);
myFunc(hello2);
myFunc(function(name) {
document.write("hi " + name);
})
</script>
3. 함수 타입의 리턴값
<script>
function createHello() {
// function hello(user) {
// document.write(user + "님 환영환영")
// }
// return hello;
return function (user) {
document.write(user + "님 환영환영<br>")
} // 위 주석을 합친 것
}
var result = createHello();
console.log(typeof result); // function
result("1.보경");
createHello()("2.보경"); // 위 두줄을 합친 것.
</script>
- createHello()("2.보경");
-> createHello() : 함수 호출 후에 아직도 함수타입이기 때문에 한번 더 호출 가능. ("2.보경");
<함수 리터럴과 익명 함수>
<함수 정의 방법 4가지>
1. 선언적 방법
2. 변수에 익명함수를 담는 방법
3. 함수 객체를 이용하는 방법(안 씀)
4. 익명함수를 선언 후 즉시 호출
<script>
function a() {
alert(0);
}
$(function() { // ready
function a() {
alert(1);
}
a();
});
$(function() { // ready
function a() {
alert("a");
}
a();
});
a(); // 0 ->1번째
$(function() { // ready
a(); // 0
})
</script>- alert 순서: 0 , 1, a , 0
- 클릭할 때마다 '안녕안녕~' 생성.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset='utf-8'>
<title>Page Title</title>
<style>
h1 {border: 1px solid; margin: 10px;}
</style>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/jquery/1.12.4/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script>
$(function(){
$("h1").click(myAppend);
function myAppend() {
$("body").append($(this).clone(true));
}
})
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>안녕안녕~</h1>
</body>
</html>
<함수 종류>
콜백 함수
- 함수 내부의 처리 결과값을 함수 외부로 내보낼 때 사용함.
- 로직 처리부분을 분리해 구현할 수 있음.
| function 함수이름 (callback) { callback(결과); } |
- 동기: 함수가 호출된 후 끝날 때까지 다음 구문을 실행하지 않고 대기하고 있는 경우.
ex. alert() 실행 후 확인 버튼을 눌러야지 다음 구문 실행 됨.
- 비동기: 함수가 호출된 후 끝날 때까지 기다리지 않고 바로 다음 구문을 실행하는 경우.
- 일반
<script>
// 사칙연산 함수
function calculator1(op, num1, num2) {
var result = 0;
switch (op) {
case "+":
result = num1 + num2;
break;
case "-":
result = num1 - num2;
break;
case "*":
result = num1 * num2;
break;
case "/":
result = num1 / num2;
break;
default:
result = "지원하지 않는 연산자.";
break;
}
document.write("두 수의 " + op + "는 " + result + "입니다.", "<br>");
}
function calculator2(op, num1, num2) {
var result = 0;
switch (op) {
case "+":
result = num1 + num2;
break;
case "-":
result = num1 - num2;
break;
case "*":
result = num1 * num2;
break;
case "/":
result = num1 / num2;
break;
default:
result = "지원하지 않는 연산자.";
break;
}
document.write("정답은 " + result + "입니다.", "<br>");
}
calculator1("+", 20, 30);
calculator2("+", 20, 30);
</script>
- 콜백함수 이용
<script>
function calculator(op, num1, num2, callback) { // 함수타입을 파라미터로 전달.
var result = 0;
switch (op) {
case "+":
result = num1 + num2;
break;
case "-":
result = num1 - num2;
break;
case "*":
result = num1 * num2;
break;
case "/":
result = num1 / num2;
break;
default:
result = "지원하지 않는 연산자.";
break;
}
callback(result);
}
function print1 (result) {
document.write("두 수의 계산결과는 "+ result + "입니다.", "<br>");
}
function print2 (result) {
document.write("정답은 " + result + "입니다.", "<br>");
}
calculator("-", 30, 15, print1);
calculator("-", 30, 15, print2);
</script>
- 미션01. 10번 버튼을 클릭하면 "완료되었습니다." 띄우기. (콜백함수 이용)
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/jquery/1.12.4/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script>
$(function() {
checkCount(showMessage);
});
function checkCount(callback){
var count=0;
$("#btnStart").click(function(){
count++;
if(count>=10)
callback();
})
}
function showMessage() {
alert("완료되었습니다.");
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<button id="btnStart">시작</button>
</body>
클로저 함수
- 변수가 메모리에서 제거되지 않고 계속해서 값을 유지하는 상태 : 클로저
- 누를 때마다 카운트 수 올라가기.
<body>
<button id="btn">클릭미</button>
<script>
function func() {
var count = 1;
document.getElementById("btn").onclick = function() {
alert("count = " + count++);
}
}
func();
</script>
</body>
- 일반 함수인 경우
<script>
function addCount() {
var count = 0 ;
count++;
return count;
}
document.write("1. count = "+addCount(),"<br>");
document.write("2. count = "+addCount(),"<br>");
document.write("3. count = "+addCount(),"<br>");
</script>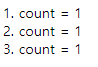
- 클로저 사용한 경우
<script>
function createCounter() {
var count = 0 ;
function addCount() {
count++;
return count;
}
return addCount;
}
var counter = createCounter();
document.write("1. count = "+ counter(),"<br>");
document.write("2. count = "+ counter(),"<br>");
document.write("3. count = "+ counter(),"<br>");
</script>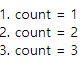
- createCounter() 함수가 호출되면 지역변수 count가 0으로 초기화됨과 동시에 만들어지고, 내부에 addCount()라는 함수도 만들어지면서 마지막으로 addCount()함수를 리턴하고 createCounter() 함수는 종료됨.
- createCounter()가 종료 되어도 addCount()함수와 count는 사라지지 않음!
'자바스크립트' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Part 03. js 코어 라이브러리(Date, Array) 21. 02. 25. (0) | 2021.02.25 |
|---|---|
| Part 03. js 코어 라이브러리(타이머 함수, Math, String) 21. 02. 24. (0) | 2021.02.25 |
| Part 02. 자바스크립트 함수기본 & 드롭다운 메뉴 만들기 21. 02. 23. (0) | 2021.02.23 |
| Part 01. 반복문 for 이어서 & 반복문 while 21. 02. 23. (0) | 2021.02.23 |
| Part 01. 04~06장- 조건문 if, switch, 반복문 for 21. 02. 22. (0) | 2021.02.22 |



